
Most Tomcat users begin by implement Form-based authentication. Those deploying applications into enterprises soon discover that those enterprises use an Active Directory and have single sign-on on all intranet sites. They eventually find Waffle, but don’t want to take the ability to do form-based logon away.
How do we give users a way to logon either way?
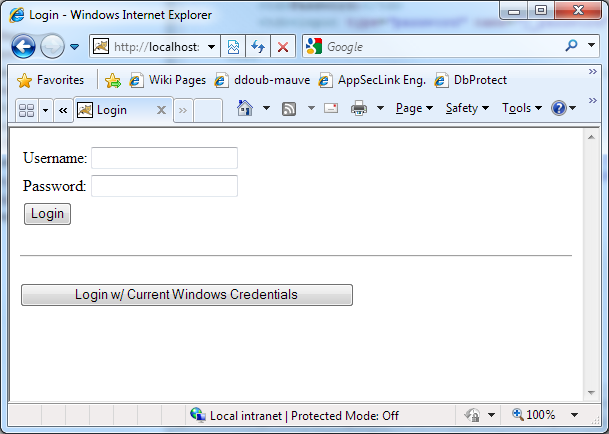
You can accomplish this with the Waffle MixedAuthenticator.
Configure Tomcat
Download and Copy Files
Download Waffle 1.3 and copy waffle-jna.jar, jna.jar and platform.jar to Tomcat’s lib directory.
Configure Mixed Authenticator Valve
Add a valve and a realm to the application context. For an application, modify META-INF\context.xml.
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8'?>
<Context>
<Valve className="waffle.apache.MixedAuthenticator" principalFormat="fqn" roleFormat="both" />
<Realm className="waffle.apache.WindowsRealm" />
</Context>
Security Roles and Constraints
Configure security roles in WEB-INF\web.xml. The Waffle Mixed Authenticator adds all user’s security groups (including nested and domain groups) as roles during authentication.
<security-role>
<role-name>Everyone</role-name>
</security-role>
Restrict access to website resources.
<security-constraint>
<display-name>Waffle Security Constraint</display-name>
<web-resource-collection>
<web-resource-name>Protected Area</web-resource-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</web-resource-collection>
<auth-constraint>
<role-name>Everyone</role-name>
</auth-constraint>
</security-constraint>
Add a second security constraint that leaves the login page unprotected.
<security-constraint>
<display-name>Login Page</display-name>
<web-resource-collection>
<web-resource-name>Unprotected Login Page</web-resource-name>
<url-pattern>/login.jsp</url-pattern>
</web-resource-collection>
</security-constraint>
Configure Form Login
Configure Form Login parameters with the location of the login page (repeated from the security constraint above) and an error page for failed logins. Modify WEB-INF\web.xml.
<login-config>
<form-login-config>
<form-login-page>/login.jsp</form-login-page>
<form-error-page>/error.html</form-error-page>
</form-login-config>
</login-config>
Login Page
Create a login page based on the following code. There are two requirements for the login form. The form-based authentication must post to any valid location with the j_security_check parameter. The destination page will be loaded after a successful login. The single sign-on form must similarly post to any valid location with the j_negotiate_check parameter in the query string.
Here’s a rudimentary example that lands an authenticated user on index.jsp.
<form method="POST" name="loginform" action="index.jsp?j_security_check">
<table style="vertical-align: middle;">
<tr>
<td>Username:</td>
<td><input type="text" name="j_username" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Password:</td>
<td><input type="password" name="j_password" /></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><input type="submit" value="Login" /></td>
</tr>
</table>
</form>
<hr>
<form method="POST" name="loginform" action="index.jsp?j_negotiate_check">
<input type="submit" value="Login w/ Current Windows Credentials" />
</form>
Demo
A demo application can be found in the Waffle distribution in the Samples\Tomcat\waffle-mixed directory. Copy the entire directory into Tomcat’s webapps directory and navigate to https://localhost:8080/waffle-mixed. Pick your method of login.
How does it Work?
Implementation details follow. Read at your own risk.
From the unauthenticated login page we are making two possible requests: one will trigger Single Sign-On and another will trigger form-based authentication. To do single sign-on we will need access to the request/response objects and to do forms authentication we will need access to the realms interface. The place where we have both is in org.apache.catalina.Authenticator.
@Override
protected boolean authenticate(Request request, Response response, LoginConfig loginConfig) {
String queryString = request.getQueryString();
boolean negotiateCheck = (queryString != null && queryString.equals("j_negotiate_check"));
boolean securityCheck = (queryString != null && queryString.equals("j_security_check"));
Principal principal = request.getUserPrincipal();
AuthorizationHeader authorizationHeader = new AuthorizationHeader(request);
boolean ntlmPost = authorizationHeader.isNtlmType1PostAuthorizationHeader();
if (principal != null && ! ntlmPost) {
return true;
} else if (negotiateCheck) {
if (! authorizationHeader.isNull()) {
return negotiate(request, response, authorizationHeader);
} else {
sendUnauthorized(response);
return false;
}
} else if (securityCheck) {
boolean postResult = post(request, response, loginConfig);
if (postResult) {
redirectTo(request, response, request.getServletPath());
} else {
redirectTo(request, response, loginConfig.getErrorPage());
}
return postResult;
} else {
redirectTo(request, response, loginConfig.getLoginPage());
return false;
}
}
Negotiate mimics the behavior of NegotiateAuthenticator, while form post follows the standard Authenticator registration process.
private boolean post(Request request, Response response, LoginConfig loginConfig) {
String username = request.getParameter("j_username");
String password = request.getParameter("j_password");
IWindowsIdentity windowsIdentity = null;
try {
windowsIdentity = _auth.logonUser(username, password);
} catch (Exception e) {
return false;
}
WindowsPrincipal windowsPrincipal = new WindowsPrincipal(windowsIdentity, context.getRealm(), _principalFormat, _roleFormat);
register(request, response, windowsPrincipal, "FORM", windowsPrincipal.getName(), null);
return true;
}

